Synthesis of low free TDI trimer
Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) can undergo trimerization under catalytic action to form trimers containing isocyanurate rings. TDI trimer has the advantages of low volatility, low toxicity, high functionality, good thermal stability, good corrosion resistance, etc. It is often used as a polyurethane curing agent in coatings and adhesives. In the 1970s, many foreign companies began to industrially produce and apply such products, such as Bayer, BASF, Dow, etc. At present, high-performance, low-free monomer TDI trimers still need to rely heavily on imports.
In this study, the catalyst NT CAT P100 was used to synthesize TDI trimer polyurethane curing agent. The experimental results show that the catalyst has the advantages of fast catalytic rate, high activity and low reaction temperature. At 40 ?, the reaction was catalyzed by dropwise addition, and the end of the reaction could be reached within 8 h, resulting in a low free monomer content TDI trimer.

NT CAT FG1021 pinhole elimination agent cell improvement agent size stabilizer foam stabilizer non-silicone silicone oil polyurethane monosodium glutamate self-skinning pinhole elimination agent
Raw materials and reagents
Toluene diisocyanate monomer TDI (80/20): industrial product, BASF; butyl acetate: analytically pure, Guangzhou Panyu Liqiang Factory; NT CAT DMP-30: industrial product, Xindian Chemical; NT CAT K-15 : Industrial products, Xindian chemistry; NT CAT P100: Xindian chemistry;
Synthesis
Under nitrogen protection, add 100 g of TDI (80/20) monomer and 100 g of butyl acetate to a dry four-necked round bottom flask equipped with a stirrer, thermometer and reflux condenser. Stir for 5 to 10 min, heat to 40°C, and add 0.5 g of catalyst in butyl acetate solution (butyl acetate 10 mL). After the dropwise addition, the temperature is controlled between 40 and 80 ?, and the reaction temperature is kept for about 8 h. The -NCO value of the reaction solution is measured every 1 h. When the -NCO content decreases to 8.5% to 9%, add 1 g Benzoyl chloride, continue the reaction for 0.5 h, stop heating and stirring, lower the temperature and discharge, to obtain a light yellow transparent liquid.
On the basis of the above process, a predetermined amount of alcohol is added dropwise, and the reaction is incubated for 30 to 60 minutes to modify the TDI trimer.
Influence of catalyst type, dosage and dropping method
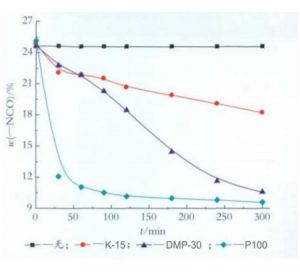
The choice of catalyst is the key to TDI trimerization. Commonly used TDI trimerization catalysts include tertiary amines, organic metal compounds, organic phosphine compounds, alkali metal carboxylates, and the like. DMP-30, K-15 and P100 were used to catalyze the reaction of 50% butyl acetate in TDI solution. The results are shown in Table 1 and Figure 2.
Table 1 Effect of different catalysts (0.5% addition) on TDI trimerization
Type of catalyst None K-15 DMP-30 P100
Reaction temperature/? 70 80 70 70
Response time/h 24 26 6 5
w(—NCO)/% 24.2 12.3 10.4 6.8
Product appearance colorless and transparent yellow transparent yellowish transparent near water white transparent
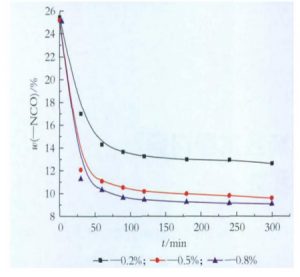
It can be seen from Table 1 and Figure 2 that without the addition of catalyst, the trimerization reaction of TDI does not occur; the effect of K-15 catalytic trimerization is poor, the temperature is higher, the reaction time is longer, and more polymers are easily produced Structure; DMP-30 and P100, both tertiary amine catalysts, have better catalytic effect. In contrast, P100 has stronger catalytic performance, and can react quickly in a short time to reduce -NCO value, and the experiment also shows that at 40 ? It still has very high catalytic activity. Therefore, P100 was selected as the catalyst. Figure 3 shows the effect of P100 catalyst dosage on TDI trimerization when they account for 2%, 0.5% and 0.8% of the total mass of TDI monomer, respectively.
Figure 2 Comparison of the catalytic efficiency of the three catalysts
It can be seen from Figure 3 that under other conditions being the same, with the increase in the amount of P100, the reaction rate is accelerated, and the content of -NCO groups is reduced. When the amount of catalyst is too small, even if the reaction time is prolonged, the -NCO content is still higher than 12%; when the amount of catalyst is too high, a large amount of residual catalyst affects the performance of the product to a certain extent. Experiments show that 0.5% of P100 is more suitable.
Figure 3 The effect of catalyst dosage on TDI trimerization
In addition, the dropping method of the catalyst will also affect the trimerization reaction. Experiments have shown that if the catalyst is added at once, the monomer reacts violently immediately, a large amount of heat is released, and the local temperature can rise by 10 ?. The increase in the activity of the reactant may cause the relative molecular mass of the product to increase and the distribution to broaden, resulting in a large amount of polymer To increase the viscosity of the product, deepen the color, and reduce the performance of the product. The method of diluting the catalyst with butyl acetate drop by drop can control the reaction temperature well.
in conclusion
P100 was used as catalyst to synthesize TDI trimer. Experiments show that the catalyst has high catalytic activity and fast catalytic rate, and its catalytic effect is better than DMP-30 and K-15.