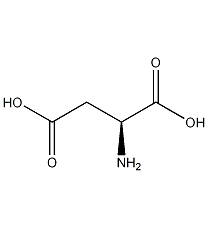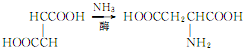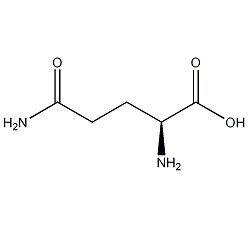
Structural formula
| Business number | 017Z |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H10N2O3 |
| Molecular weight | 146.15 |
| label |
L-Glutamic acid-5-amide, L-aminocarbonylbutyrine, L-2-Aminoglutaric acid amide, (S)-(+)-Glutamine, L-Glutamic acid 5-amide, amino acid drugs, intermediates, Biochemical reagents |
Numbering system
CAS number:56-85-9
MDL number:MFCD00008044
EINECS number:200-292-1
RTECS number:MA2275100
BRN number:1723797
PubChem number:24277983
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless needle-like crystals
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4?): 1.321
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL , air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC, decomposition): 185?186
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 185
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): 32.25° (c=10, 2 N HCl).
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturation Vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (% , V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: soluble in water, almost insoluble in methanol, Ethanol, ether, benzene, acetone, ethyl acetate and chloroform, etc.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Men’s oral TDLo: 27mg/kg/1W-I; Rat’s oral LD50: 7500mg/kg; Mice’s oral LD50: 21700mg/kg 2. Other multi-dose toxicity: Rat’s oral TDLo: 260mg/kg/30D-I 3. Mutagenicity: sister chromatids exchangeTEST system: human lymphocytes: 10mg/L
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index:33.83
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 110.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 313.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 64.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 13.41
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -3.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 106
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 146
10. Isotopes Number of atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 1
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine chemical bonds Number of stereocenters: 0
14. Number of stereocenters of uncertain chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Participate in the biosynthesis of glucosamine, a component of mucin in the digestive tract mucosa, thereby promoting the repair of mucosal epithelial tissue and helping to eliminate ulcer lesions. At the same time, it can promote brain metabolism and improve brain function through the blood-brain barrier. Like glutamate, it is an important nutrient for brain metabolism.
2. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke.
3. Valuable in the field of immunity. After the body converts toxic ammonia into non-toxic glutamine, it is excreted through urine. Generally not involved in the composition of proteins.
Storage method
This product should be stored in a sealed, cool place and away from light.
Synthesis method
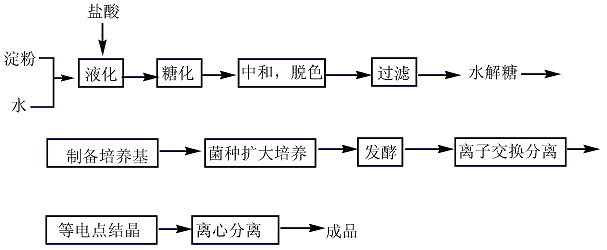
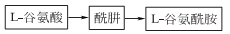
L-Glutamine widely exists in nature. For example, it is contained in free state in pumpkin and sunflower seedlings, and its N-ethyl compound (theanine) is contained in tea leaves. Although glutamine can be extracted from natural products, fermentation and synthesis are used for mass production. 1. Synthesis method: It is obtained by condensation, addition, salt formation and hydrolysis of L-glutamic acid-5-methyl ester ([1499-55-4]). Glutamic acid is esterified with methanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, and the resulting esterified liquid is added dropwise to the mixture of methanol and carbon disulfide. While adding dropwise, ammonia is circulated under cooling. After the esterification liquid is added dropwise, continue to pass ammonia, then add triethylamine, and leave it sealed at 30°C for 40 hours. After concentrating under reduced pressure to drive out ammonia, a concentrated solution of ?-methyl ester-L-glutamic acid-N-amino acid diammonium salt was obtained. Heat it to 40-45°C and add acetic acid. After stirring for 30 minutes, carbon disulfide was removed under reduced pressure, and a large amount of crystals precipitated. Then add an equal volume of methanol, place it at 0°C for 12 hours, and filter to obtain crude glutamine. The finished product is obtained through activated carbon decolorization and recrystallization. 2. Fermentation method uses glucose, acetic acid, and ethanol as the carbon source of the culture medium, and uses Brevibacterium flavum for fermentation. The yield based on glucose is 39g/L, and the yield is 39%.
2.Synthesis
3.Fermentation method

4. Extracted from the cell wall of fungi.
Purpose
1. This product is converted into sugar amine in the body, which serves as a precursor for mucin synthesis and can promote ulcer healing. It is mainly used as a peptic tract ulcer drug. In addition, it can also be used as a brain function improver and in the treatment of alcoholism.
2.It is used to improve the brain function of children with mental retardation and patients with mental disorders, alcoholism and epilepsy.
3. Nutritional supplements. In medicine, it is used to treat digestive organ ulcers (gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers) and acute and chronic gastritis. It is also used as a brain function improver and to treat alcoholism.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/72
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Lupragen-N205-MSDS.pdf
extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/3-morpholinopropylamine/
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-ncm-catalyst-cas110-18-9-newtopchem/
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44436
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/hard-foam-catalyst-smp/
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1734
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39408
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/51.jpg
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-tetn-catalyst-cas280-57-9-evonik-germany/