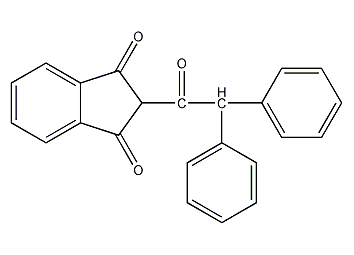
Structural formula
| Business number |
01T2 |
| Molecular formula |
C23H16O3 |
| Molecular weight |
340.37 |
| label |
2-(2,2-Diphenylacetyl)-1,3-indandione,
Diphacin sodium,
Dibenzofen,
enemy rats,
wild squirrel net,
Didandin,
Dipaxin,
Diphenacin,
Rodenticide
|
Numbering system
CAS number:82-66-6
MDL number:None
EINECS number:201-434-5
RTECS number:NK5600000
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow powder, the pure product is odorless and tasteless, the original drug has a slight smell
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4?): Uncertain
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Uncertain
4. Melting point (ºC): 145~147
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Uncertain
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Uncertain
7 . Refractive index: Uncertain
8. Flash point (ºC): Uncertain
9. Specific rotation (º): Uncertain
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Uncertain
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Uncertain
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Uncertain Determine
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Uncertain
15. Critical pressure (KPa ): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19. Solubility: soluble in alcohol and acetone, soluble in hot water, insoluble in benzene and toluene.
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity:
Rat caliber LD50: 1500 ug/kg; rat inhalation LC50: 2 gm/m3/4H
Rat skin LD50: 200mg/kg; Rat LD50: 11mg/kg;
Mouse LD50: 28300 ug/kg; Mouse LD50: 300mg/kg
Dog LD50: 3mg/kg;
Cat caliber LD50: 15mg/kg;
Rabbit caliber LD50: 35mg/kg;?
Pig caliber LD50: 1?mg/kg;?
Duck caliber LD50: 3158mg/kg;
Breeding animal LD50: 910ug/kg;
Ecological MathematicsAccording to
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 96.78
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 267.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 731.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 56.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 38.56
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: 5
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 51.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 26
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 512
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
The sodium salt (often called diphacin sodium salt) has a solubility of 5% in water at 100°C. It changes from yellow to red when heated to 207-208°C and decomposes at 325°C.
Storage method
Stored sealed and protected from light.
During storage and transportation, it must be protected from moisture and sunlight, kept ventilated, and must not be mixed with food, seeds, or feed.
Synthesis method
1. Preparation of phenylacetone. Industrially, phenylacetamide is used as raw material and reacted at 110-130°C for 2 hours in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain phenylacetic acid. Phenylacetic acid and acetic anhydride react under the catalysis of anhydrous sodium acetate at 140-150°C for 18 hours. The acetic acid generated continues to steam out. After the reaction, add an appropriate amount of cold water and separate the water layer. The crude phenyl acetone is dissolved in 100% sodium hydroxide with 20% sodium hydroxide. Stir at ~110°C for 2 hours, and control the pH value to 12.
2. Preparation of diphenyl acetone. Add bromine dropwise into the phenyl acetone mixture, and control the temperature to less than 30°C to prevent incomplete bromination caused by excessive volatilization of bromine. After the reaction is completed, remove the residual Hydrogen bromide. Then, the generated bromide is added dropwise to the pure benzene liquid under negative pressure, and anhydrous aluminum trichloride is used as the catalyst. The reaction is carried out at room temperature for 3 to 4 hours, and then post-processed to obtain diphenylacetone.
3. Synthesis of diphacin and diphacin sodium salt. Put the solvent toluene and the catalyst sodium methoxide into the reaction pot, raise the temperature to 110°C, add dimethyl phthalate and toluene mixture after azeotropy, and add diphenyl diphenyl dropwise Add a toluene mixture of acetone and react at 100-120°C for 1.5-2 hours.
In acidic or neutral media, the product obtained is diphacin, and in alkaline medium, diphacin sodium salt is obtained. Sodium methoxide is a strong base, and its amount determines the ratio of the two products (diphacin and diphacin sodium salt).
4.Phenyl acetone is generated from the acylation reaction of phenylacetic acid and acetic anhydride, and phenyl acetone is generated through bromination and phenylation reactions. Diphenyl acetone. Then, the solvent toluene and the catalyst sodium methoxide are put into the reactor, and after azeotropy, a mixture of dimethyl phthalate and toluene is added, and a toluene mixture of partial diphenylacetone is added dropwise. In acidic or neutral media, the product is dimethonium, and in alkaline medium, dimethin sodium salt is obtained.
Purpose
1. Chronic rodenticide. It is the first generation anticoagulant that is widely used. It has broad target spectrum, good palatability, slow action and obvious effect. When a lethal dose is taken, it destroys the hyperthrombin in the blood of rats, prolongs the coagulation time, and causes massive internal bleeding and hypoxia in the rat’s internal organs. Therefore, most rats will run out of the hole before death and become listless and sluggish until they die. Used to kill domestic rats in residences, grain depots, vehicle and ship docks and other places. It can also be used to kill wild rats in dry fields, rice fields, forest areas and grasslands. Use 0.25‰~0.5‰ poisoning for multiple times in a row. You can also use 1‰ poison bait once. Most poisonous baits are prepared with rice or noodles, but you can also use sweet potato shreds, carrot shreds and other baits. For other foods that rats like to eat, add 2% to 5% cooking oil for better results. For example, the preparation of 0.5‰ rice bait: Dissolve 0.5g of diphacin sodium salt in an appropriate amount of hot water (above 80°C), soak it in 1000g of rice to evenly absorb the agent, and dry it to make rice bait. Or dissolve 0.5g of diphacin sodium salt in an appropriate amount of hot water, mix it with 1000g of flour and bake it into dough cakes to make dough bait.
2.It is an anticoagulant rodenticide. It has broad target spectrum, good palatability, slow action and obvious effect. When a lethal dose is taken, it destroys the hyperthrombin in the blood of rats, prolongs the coagulation time, and causes massive internal bleeding and hypoxia in rats until death. Used to kill domestic rats in residences, grain depots, vehicle and ship docks and other places. It can also be used for rodent control in dry fields, rice fields, forest areas and grasslands. Most poisonous baits are prepared with rice or noodles, but sweet potato shreds, carrot shreds and other baits can also be used.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/64extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat9201-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-c-124-low-odor-tertiary-amine-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/138-3.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/3164-85-0/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat4210-catalyst-cas-683-18-1-dibutyltin-dichloride/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/71.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/coordinated-thiol-methyltin/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40422extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44919