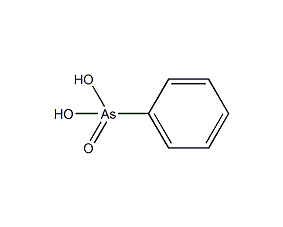

Structural formula
| Business number | 02D6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H7AsO3 |
| Molecular weight | 202.04 |
| label |
Ai3-16050[qr], Arsonicacid,phenyl-, Arsonicacid,phenyl-[qr], Kyselinabenzenarsonova, Monophenylarsonic acid, Phenylarsenic acid, Phenyl-arsonicaci, Phenylarsonic acid[qr] |
Numbering system
CAS number:98-05-5
MDL number:MFCD00002097
EINECS number:202-631-9
RTECS number:CY3150000
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: White crystalline powder.
2. Density (g/mL,25?): 1.76
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL,air =1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 160
5. Boiling point (ºC,normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Not determined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flashpoint (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC?: Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 55ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 25 ºC): Not determined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/Log value of the partition coefficient (water): undetermined
17. Explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Undetermined
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 50mg/kg;
MouseOral LD50?270?g/kg;
-US; mso-fareast-language: ZH-CN; mso-bidi-language: AR-SA”>Rabbit intravenous injectionLD50:16mg/kg;
Ecological data
It is extremely harmful to water and toxic to fish. Do not let the product enter the water body.
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP):
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 57.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 145
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. The number of uncertain atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Does not decompose under normal temperature and pressure. Avoid contact with oxidants.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and equipment that are prone to sparks
Tools. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
After diazotization of aniline and Arsenous acid reaction is obtained.
Purpose
is used as an analytical reagent.
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/88-1.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39941extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44279extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/bismuth-octoate/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/catalyst-a400-polyurethane-catalyst-a400/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44374extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-ne600-catalyst-cas10861-07-1-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Lupragen-N205-MSDS.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/drier-butyl-tin-oxide-fascat-4101/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/dabco-dc2-delayed-catalyst-dabco-dc2/