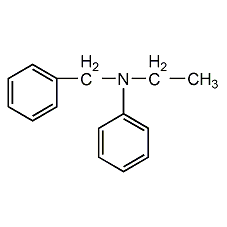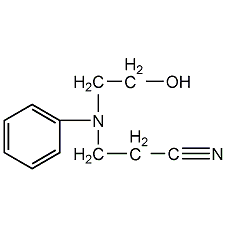
Structural formula
| Business number | 024Z |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C11H14N2O |
| Molecular weight | 190.24 |
| label |
N-(2-cyanoethyl)-N-hydroxyethylaniline, 3-[(2-hydroxyethyl)phenylamino]propionitrile, N-(2-cyanoethyl)-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)aniline, N-Cyanoethyl-hydroxyethyl aniline |
Numbering system
CAS number:92-64-8
MDL number:MFCD00035705
EINECS number:202-174-5
RTECS number:UG2905000
BRN number:2369849
PubChem number:24874374
Physical property data
1. Properties: Oily liquid.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4?): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): Not determined
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Not determined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Not determined Determined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturation Vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (% ,V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Undetermined
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 55.91
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 167.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 453.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 53.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 22.16
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 47.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 14
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 191
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12.??Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
None
Storage method
This product should be kept sealed.
Synthesis method
None
Purpose
Used in the production of dyes such as Disperse Red S-FL and Disperse Red 3GFL.
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/hydroxy-NNN-trimethyl-1-propylamine-formate-CAS62314-25-4-catalyst-TMR-2.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40517extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nnnn-tetramethyl-16-hexanediamine/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dioctyl-dimaleate-di-n-octyl-tin/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/173extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/delayed-catalyst-for-foaming-dabco-dc2-polyurethane-catalyst-dabco-dc2/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/2-ethylhexanoic-acid-potassium-CAS-3164-85-0–K-15.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/polycat-8-catalyst-cas10144-28-9-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/butyltin-acid/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40454