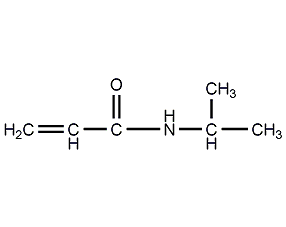
Structural formula
| Business number | 02Z9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H11NO |
| Molecular weight | 113.16 |
| label |
N-(1-methylethyl)-2-acrylamide, N-isopropylacrylamide smart monomer, Isopropyl acrylamide, Isopropylamid kyseliny akrylove, 2-Propenamide-N-(1-methylethyl)-, NIPAM, H2C=CHCONHCH(CH3)2, acrylamide derivatives, Smart material monomer, temperature sensitive materials |
Numbering system
CAS number:2210-25-5
MDL number:MFCD00041913
EINECS number:218-638-5
RTECS number:AS3675000
BRN number:None
PubChem number:24865991
Physical property data
1. Properties: White to light yellow solid
2. Density (g/mL, 25ºC): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air =1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 60-63
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6 . Boiling point (ºC, 2mmHg): 89-92
7. Refractive index (nD20): Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºF) : Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 100ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/water) distribution Log value of coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: soluble
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: rabbit, eye contact, standard Draize test: 100mg, moderate reaction 2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 375mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 419mg/kg; mouse abdominal cavity LDLo: 500mg/kg; rabbit skin contact LDLo: 1580mg/kg3. Other multi-dose toxicity: oral TDLo in mice: 2173mg/kg/8W-I4. Reproductive toxicity: oral male mice, mated 16 days ago TDLo: 2235mg /kg; Orally administered to male mice, TDLo after mating 5 weeks ago: 238mg/kg; Oral administration to male mice, TDLo after mating 5 days ago: 158mg/kg 5. Mutagenicity: Sperm morphology test: Orally administered to mice: 238mg/kg kg/5W
Ecological data
Slightly hazardous to water. Do not allow undiluted or large quantities of product to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems. Do not discharge material into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 33.15
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 128.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 290.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 25.6
5. Polarizability: 13.14
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.9
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 29.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 96.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Storage method
Refrigeration should be stored in a cool, dry place. Store in an airtight container. Low temperature preservation
Synthesis method
1. Acryloyl chloride and isopropylamine are used as raw materials and reacted under the conditions of ethyl acetate. C3H7NH2+CH2CHCOCl——CH2? CHCONHCH(CH3)2+HCl uses ethyl acetate or benzene as the medium, and isopropylamine (IPA) and acryloyl chloride (ACC) as raw materials. Obtain CH2=CHCONHCH(CH3)2 crude product, and then recrystallize it through n-hexane to obtain high-purity CH2 sub>=CHCONHCH(CH3)2. The yield is approximately 88%. 2. Acrylonitrile and isopropyl alcohol are used as raw materials and react under concentrated sulfuric acid conditions. CH2=CHCN+(CH3)2CHOHCH2—–CHCONHCH(CH 3)
Mix 0.15 mol acrylonitrile, 0.15 mol isopropanol, 3×10-4mol parahydroxyanisole and pour into a 250mL four-necked flask , pour 0.45 mol of concentrated sulfuric acid into the funnel and drip it from one side port. A thermometer and a condenser tube are installed at the other two side ports. A stirrer is installed in the middle bottle mouth, and the stirring speed is controlled at 100r/min. Adjust the dripping speed of concentrated sulfuric acid in the funnel so that the control temperature in the reaction bottle is between 55 and 65°C. The dripping time is about 60 minutes. After continuing the reaction for 30 minutes, the color of the reaction solution will be light yellow.
The reaction solution is neutralized with ammonia water to pH=1~2. After neutralization, the reaction solution is divided into three layers. The water layer and the oil layer are put into two beakers respectively. The water layer is fully frozen to make NIPAM single. The solid crystallizes and floats on the water layer, and the ammonium sulfate crystals precipitate at the bottom of the beaker; the oil layer is fully frozen to make it agglomerate. Then, the oil layer agglomerates and the water layer NIPAM crystals are filtered under reduced pressure and placed in a vacuum oven to dry at room temperature. Then use benzene-n-hexane mixed solvent to recrystallize at least 3 times to obtain white crystalline NIPAM with a yield of 54.2%.
Purpose
N-Isopropylacrylamide is an acrylamide derivative monomer. Due to the hydrophilic amide group and hydrophobic isopropyl group in the molecule, the homopolymer has a low critical solution temperature and other good properties. Characteristics, mainly used to manufacture polymer gels with temperature-sensitive properties, such as: drug controlled release materials, enzyme solid materials, dehydrating agents, concentrates, etc. It can also be used to make modified latex, special coatings, adhesives, etc.
extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/organic-bismuth-catalyst-dabco-mb20-dabco-mb20/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-46-PC-CAT-TKA-catalyst–46.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/cas-68928-76-7/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/toyocat-ets-foaming-catalyst-tosoh/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/74extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/high-quality-cas-110-95-2-tetramethyl-13-diaminopropane-tmeda/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39748extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/category/morpholine/page/5392/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/68extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-MP602-delayed-amine-catalyst-non-emission-amine-catalyst.pdf