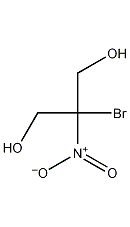
Structural formula
| Business number | 015G |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H6BrNO4 |
| Molecular weight | 199.99 |
| label |
Bronopropanol, Mixed with cotton alcohol, Blobol, Pilebao, Bronopol propylene glycol, Bronopol wettable powder, bacteriostatic alcohol, bronopol, Brobol, Bubol, Bronocot, Bronopolu, Bronotak, Fungicide |
Numbering system
CAS number:52-51-7
MDL number:MFCD00007390
EINECS number:200-143-0
RTECS number:TY3385000
BRN number:1705868
PubChem number:24850626
Physical property data
1. Properties: The pure product is a yellow-brown solid. What precipitates from the mixed solution of ethyl acetate and chloroform is white crystal, odorless and tasteless.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4?): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 130
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 1.68×10-3
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature ( ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in petroleum, slightly soluble in chloroform, acetone and benzene, soluble in water, ethanol and ethyl acetate
Toxicological data
LD50 (mg/kg): acute oral administration in rats is 180-400, in mice is 270-400, and in dogs is 250. Dabai is an acute percutaneous disease of more than 1,600.
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 32.73
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 99.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 290.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 74.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 12.97
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 86.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 107
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
When the aqueous solution is alkaline, it will decompose slowly and cannot be used with certain metals such as aluminum. It is moderately irritating to rabbit skin and mildly irritating to eyes. Animal tests show no teratogenic, carcinogenic or mutagenic effects.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dry place.
Synthesis method
Obtained from the reaction of nitromethane with formaldehyde and bromine. There are two operating processes. (1) Add nitromethane, 30% formaldehyde, calcium chloride and sodium hydroxide to the reaction device in a molar ratio of 1:2:2:2, stir, and add bromine and dichloroethane dropwise below 0°C to prepare the mixture. The solution. After the addition is completed in 1 hour, the amount of bromine used is equimolar to that of nitromethane. Separate the dichloroethane layer and evaporate the dichloroethane. Obtain white solid (crude product). The aqueous layer of the reactant was extracted with diethyl ether, and the diethyl ether in the diethyl ether extract was evaporated to obtain a part of the crude product. Combine the crude products and recrystallize them with diethyl ether to obtain the pure product. (2) First prepare 2-nitro-1,3-propanediol, add nitromethane and 30% formaldehyde solution to the reflux reaction device in a molar ratio of 1:2, then add 2% potassium carbonate, heat to reflux for 1 hour, cool and precipitate crystals . Extract with ether, dry, and evaporate the ether to obtain 2-nitro-1,3-propanediol. Then dissolve it in methanol, add 20% sodium methoxide methanol solution, stir at 20°C, and precipitate sodium 2-nitro-1,3-propanedioxide. Filter out the sodium salt and suspend it in dry diethyl ether. Bromination: Add bromine dropwise to the diethyl ether suspension of sodium 2-nitro-1,3-propanediol below 0°C, and stir for 10 minutes after the drops are completed. Filter and evaporate the ether to obtain 2-bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol.
Put measured amounts of nitromethane, formaldehyde, water and ethanol into the reaction kettle, add 40% liquid caustic soda dropwise under cooling, when solids precipitate, then Add a certain amount of bromine dropwise, stir after addition, evaporate part of the water and ethanol under reduced pressure, and obtain bronopol after cooling, crystallization, filtration, and drying. The yield is ?70% and the content is about 93%.
Purpose
1. Cosmetic preservatives are added during the processing of cosmetics such as shampoos, balms and creams. The bactericidal concentration in cosmetics is 0.01%-0.02%. It can also be used in detergents, fabric treatment agents, etc.
2.Bactericide. It can effectively prevent and control a variety of plant pathogenic bacteria. Treatment of cotton seeds can prevent and control cotton black arm disease and bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas angularis and has no phytotoxicity to cotton. It can also be used for rice bakanae disease. The recommended concentration is 800~1000 mg/L.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/42950extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44193extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44677extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/high-quality-nn-dicyclohexylmethylamine-cas-7560-83-0/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dimethyltin-dichloride/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/rc-catalyst-108-cas108-39-4-rhine-chemical/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/size-stabilizer/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat9201-catalyst-dibutyl-tin-oxide-fascat9201/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/synthesis-of-low-free-tdi-trimer/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/toluene-diisocyanate-tdi-tdi-trimer/