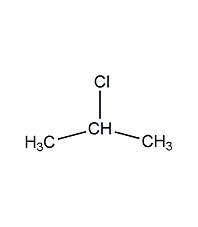
Structural formula
| Business number | 01JE |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H7Cl |
| Molecular weight | 78 |
| label |
Isopropyl chloride, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-29-6
MDL number:MFCD00000867
EINECS number:200-858-8
RTECS number:TX4410000
BRN number:1730782
PubChem number:24845308
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless transparent liquid [1]
2. Melting point (ºC): – 117.2[2]
3. Boiling point (ºC): 35.7[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.86 (20ºC) [4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 2.71[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 68.7 (25.5ºC) [6]
7. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): -2014.8[ 7]
8. Critical temperature (ºC): 212[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.72[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.9[10]
11. Flash point (ºC): -32 (CC)[11]
12. Ignition temperature (ºC): 593[12]
13 . Explosion upper limit (%): 10.7[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%): 2.8[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in methanol, ether and benzene. [15]
16. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC): 0.001591
17. Critical density ( g·cm-3): 0.325
18. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 242
19. Critical compression factor: 0.527
20. Eccentricity factor: 0.224
21. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 26.29
22. Heat of fusion (KJ/kg): 94.12
23. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): 164.1
24. Heat of combustion (KJ /mol, 25ºC, liquid): 2018.04
25. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 8.399
26. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 206.4
27.Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5?16.455
28.van der Waals area (cm2 ·mol-1): 6.610×109
29. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 45.740
30. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -172.1
31. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 133.7
32. Gas phase Standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -144.8
33. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K -1): 306.05
34. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -61.3
35. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 87.56
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity Rat caliber LD50: 5mg/kg; Rat inhalation LC50: 120mg/m3; Mouse caliber LD50: 1300mg/kg; Mouse inhalation LCLO: 119mg/m3;
2. Other multi-dose toxicity data Rat inhalation LC50: 236 gm/m3/30M/1W-I;
3. Teratogenicity Salmonella: 1 gm/plate;
4 , has a strong anesthetic effect and damages the liver and kidneys, but…??The irritation effect on skin and mucous membranes is very light.
5. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 5g/kg (rat Oral); 1300mg/kg (oral in mice)
LC50: 120g/m3 (rat inhalation)
6. Irritation No information available
7. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Rat, Rabbits, mice, guinea pigs and monkeys inhaled 3.21g/m3, 7 hours a day, 5 days a week, 127 times. The animals all survived, with no abnormalities in growth and appearance. Some animals have pathological changes in liver and kidneys.
8. Mutagenicity[18] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 1g/dish.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 17d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.75
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 89.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 187.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 18.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.22
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 10.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. When burned, toxic gases such as phosgene are generated. It decomposes into propylene and hydrogen chloride at high temperature (about 400°C). Isopropyl alcohol is produced during hydrolysis. Because the chlorine atoms in its structure are very active, they can react with aromatic amines and aliphatic amines, and remove hydrogen chloride to form N-isopropyl aromatic amines and isopropyl aliphatic amines. The chlorine atoms are hydrolyzed to form isopropyl alcohol.
2. Vapor and liquid can irritate skin, eyes and respiratory system. It has an anesthetic effect at high concentrations and can depress the central nervous system. Long-term exposure can cause damage to the liver and kidneys.
3. Stability[20] Stable
4. Prohibited use Substances[21] Strong oxidants, strong bases
5. Conditions to avoid contact[ 22] Heating
6. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
7. Decomposition products[24] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 29°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Obtained from the reaction of propylene and anhydrous hydrogen chloride. Mix dry hydrogen chloride and propylene at a molar ratio of 1:1.2, pass them into a reactor equipped with an activated clay catalyst, react at 120-140°C, and condense the product to obtain 2-chloropropane. The yield is 65%. It can also be obtained by the reaction of isopropyl alcohol and hydrogen chloride in the presence of zinc chloride.
?Preparation method?
?1. Isopropyl alcohol chlorination method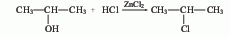
?2. Addition method of propylene and hydrogen chloride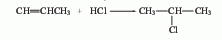
Purpose
1. Organic synthetic raw materials, used to make the pesticide piclochlor and also used as solvents. Used as a solvent for fats and oils and as a special solvent for organic synthesis. It is also used as a raw material for the manufacture of surgical anesthetics and thymol.
2. Used as a solvent and used in the manufacture of isopropylamine. [26]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1145extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/delayed-amine-a-400-niax-catalyst-a-400/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/129-2.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/catalyst-a-300/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nn-dimthylbenzylamine/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/FASCAT4350-catalyst-FASCAT-4350.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/134-1.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/595extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-MB20-bismuth-metal-carboxylate-catalyst-catalyst–MB20.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-la-300-catalyst-cas10861-07-1-newtopchem/