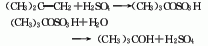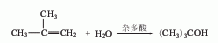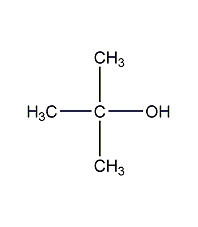
Structural formula
| Business number |
01JY |
| Molecular formula |
C4H10O |
| Molecular weight |
74 |
| label |
trimethylmethanol,
2-Methyl-2-propanol,
Trimethylcarbinol,
2-Methyl-2-propanol,
tert-Butyl alcohol,
Aliphatic alcohols, ethers and their derivatives
|
Numbering system
CAS number:75-65-0
MDL number:MFCD00004464
EINECS number:200-889-7
RTECS number:EO1925000
BRN number:906698
PubChem number:24870757
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless crystal or liquid with camphor smell. [1]
2. Melting point (?): 25.7[2]
3. Boiling point (?): 82.4 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.784[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 2.55[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 4.1 (20?)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2630.5[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.97[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.35[9]
10. Flash point (?): 11 (CC)[10]
11. Ignition temperature (?): 470[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%) : 8.0[12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.4[13]
14. Solubility: Soluble in water, ethanol and ether. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 3.35
16. Heat of fusion (KJ/kg): 91.6
17. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 27ºC, constant pressure): 3.04
18. Electrical conductivity (S/m): 2.9×10-7
19. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC): 0.00133
20. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.382330
21. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.270
22. Critical Volume (cm3·mol-1): 275
23. Critical compression factor: 0.259
24. Eccentricity factor :0.616
25. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 5.9095
26. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 334.79
27. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 21.492
28. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 7.620×109
29. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol– 1): 52.380
30. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 2690.77
31. Gas phase Standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -312.42
32. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K -1): 326.70
33. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -177.6
34. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 113.63
35. Liquid phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2643.95
36. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): – 359.24
37. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 192.88
38. Liquid phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1):-184.68
39. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 218.6
40. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2637.26
41. Crystal phase standard claim heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -365.89
42. Crystal phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1) : 170.58
43. Crystal phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): 184.68
44. Crystal phase standard hot melt (J· mol-1·K-1): 146.1
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[15]
LD50: 2743mg/kg (rat oral); >2g/kg (rabbit oral Skin)
LC50: >10000ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation[16]
Rabbit transdermal: 500?l (24h), mild stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 100?l (24h), severe irritation.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability[17]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 677~4320
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 2400~12000
3. Non-biodegradability[18]
Half-life of photooxidant in water (h): 18480~5.70×108
Light in air Oxidation half-life (h): 59~590
4. Other harmful effects [19] This substance is harmful to the environment, special attention should be paid to water bodies of pollution.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 22.08
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 92.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 203.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 23.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.75
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.5
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 25.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It has the chemical reaction characteristics of tertiary alcohol. Biprimary alcohol and secondary alcohol are prone to dehydration reaction, and shaking with hydrochloric acid is prone to generate chloride. Non-corrosive to metals.
2. It can form an azeotropic mixture with water, with a water content of 21.76% and an azeotropic point of 79.92°C. Adding potassium carbonate to the aqueous solution can make it stratified. It is flammable, and its vapor and air can form an explosive mixture, which can cause combustion and explosion when exposed to open flames or high heat. It can react with oxidants.
3. Stability[20] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[21] Acids, acid anhydrides, strong oxidants
5. Polymerization hazards[22] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Sulfuric acid hydration method consists of hydrating isobutylene and sulfuric acid: Generally, the mixed C4 fraction after extracting butadiene is used as raw material, and esterified with 60-70% sulfuric acid under the conditions of 0.7MPa and 15?, 99 % of the isobutylene is absorbed to form tert-butyl sulfate, which is then hydrolyzed to form tert-butyl alcohol. After steam desorption, the water is removed, and the finished product is refined and purified.
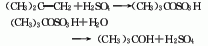
2. Ion exchange resin hydration method The C4 fraction and soft water are mixed and hydrated in the presence of cation exchange resin to generate tert-butanol. After layering and concentration, 85% tert-butanol is obtained.
3. Use the mixed C4 fraction after extracting butadiene as raw material, esterify it with 60% to 70% sulfuric acid, and 99% of the isobutylene is absorbed to form tert-butyl sulfate, which is then hydrolyzed to form Tert-butyl alcohol is desorbed by water vapor, separated from the water, and refined and purified to obtain the finished product. Or mix the C4 fraction and soft water and hydrate it in the presence of cation exchange resin to form tert-butanol, which can be separated and concentrated to obtain tert-butanol. 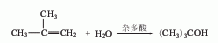
4. Use industrial product tert-butyl alcohol as raw material, first use saturated Wash with sodium bicarbonate solution, then add 10% sodium hydroxide solution to reflux and distill together. The distillate is dehydrated and dried with anhydrous potassium carbonate. Add newly calcined calcium oxide to the clear liquid obtained by filtration, reflux and distill. The distillate is Add tartaric acid and then distill, and collect the 81.5-83.5°C fraction, which is the finished product.
Purpose
1. OftenIt can replace n-butanol as a solvent for coatings and pharmaceuticals. Used as fuel additive for internal combustion engines (to prevent carburetor icing) and antiknock agent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis and an alkylation raw material for the production of tert-butyl compounds, it can produce methyl methacrylate, tert-butylphenol, tert-butylamine, etc., and is used to synthesize drugs and spices. Isobutylene with a purity of 99.0-99.9% can be produced by dehydrating tert-butyl alcohol. It is used as a solvent for industrial detergents, pharmaceutical extractants, pesticides, wax solvents, cellulose esters, solvents for plastics and paints, and is also used in the manufacture of denatured alcohol, spices, fruit essence, isobutylene, etc.
2. Solvents and chromatographic analysis reference substances used to determine molecular weight. In addition, it is often used as a solvent for coatings and pharmaceuticals instead of n-butanol. Used as fuel additive for internal combustion engines (to prevent carburetor icing) and antiknock agent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis and an alkylation raw material for the production of tert-butyl compounds, it can produce methyl methacrylate, tert-butylphenol, tert-butylamine, etc., and is used to synthesize drugs and spices. Dehydration of tert-butyl alcohol can produce isobutylene with a purity of 99.0% to 99.9%.
3. Used in organic synthesis, manufacturing flavors, etc. [24]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/34.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39757extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/self-skinning-pinhole-elimination-agent/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/586extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/935extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-T-12-tin-catalyst-NT-CAT-T-120–T-12.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat-4224-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Butyl-tin-thiolate-10584-98-2-CAS-10584-98-2-Butyltin-mercaptide.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/catalyst-c-225/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/44