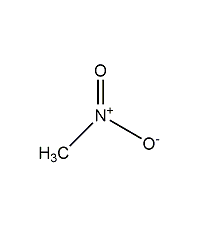
Structural formula
| Business number | 01JP |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH3NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 61.04 |
| label |
Nitrocarbol, Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-52-5
MDL number:MFCD00007400
EINECS number:200-876-6
RTECS number:PA9800000
BRN number:1698205
PubChem number:24845304
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless oily liquid with fruity aroma. [1]
2. pH value: 6.12 (0.01mol/L aqueous solution) [2]
3. Melting point (?): -29[3]
4. Boiling point (?): 101.2[4]
5. Relative density (water=1): 1.14[5]
6. Relative vapor density (air=1): 2.11[6]
7. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 3.71 (20?)[7]
8. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -708.1[8]
9. Critical temperature (?): 315[9]
10. Critical pressure (MPa): 6.30 [10]
11. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -0.35[11]
12. Flash point ( ?): 35 (CC) [12]
13. Ignition temperature (?): 418[13]
14. Explosion upper limit (%): 63.0[14]
15. Explosion lower limit (%): 7.1[15]
16. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, and dimethylformamide. [16]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[17]
LD50: 940mg /kg (orally in rats); 1440mg/kg (orally in mice)
2. Irritation No information available
3 .Carcinogenicity [18] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G2B, suspected human carcinogen.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[19]
LC50: 460mg/L (48h) (zebrafish, static); <278mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow, static)
2. Biodegradability [20] Sealed bottle test, initial concentration 2ppm, after 4 weeks Degradation is 4%, initial concentration is 10ppm, degradation is 5% after 4 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability No information available
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 12.70
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 57.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 130.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 25.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 5.03
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 45.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 27.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertainty principle?Number of stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15 .Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Colorless oily liquid. Miscible with alcohol, ether, carbon tetrachloride, dimethylformamide and other organic solvents. It can dissolve dyes, greases, waxes, cellulose derivatives, resins, etc., especially has good dissolving ability for nitrocellulose and cellulose acetate. Can dissolve aromatic hydrocarbons, but does not mix with alkanes and cycloalkanes. This selective characteristic can be used for the separation of hydrocarbons and the refining of lubricating oils. Nitromethane and all nitroalkanes readily dissolve anhydrous aluminum chloride and can produce solutions with a content of approximately 50%. The addition product AlCl3-RNO2 formed after dissolution is used in the alkylation reaction of hydrocarbons, and its catalytic effect is stronger than aluminum trichloride. Its aqueous solution is slightly acidic. This product is flammable and explosive. Wear protective equipment when operating. It does not absorb moisture and may explode in case of violent impact.
2. Chemical properties: Use litmus paper to test that the nitromethane aqueous solution is acidic, that is, the pH of a 0.01mol/L aqueous solution is 6.12; the pH of a saturated aqueous solution is 4.01; and the pH of water-saturated nitromethane is 4.82. Nitromethane has tautomerism and contains a trace amount of acid nitrostructure. The tautomerism constant in water is KT=1.1×10-17. The hydrogen atom on the oxygen atom in the acid nitrate formula is very active and can easily generate protons, so it is acidic and can react with strong bases to form salts. The sodium salt formed by nitromethane and sodium hydroxide is explosive. This sodium salt can undergo nucleophilic addition with aldehydes to form ?-nitroalcohol. For example, it can be added with formaldehyde in an alkaline solution to obtain ?-nitroethanol. . ?-Nitroalcohol is easily dehydrated into unsaturated nitro compounds, such as nitromethane and benzaldehyde to generate ?-nitrostyrene. In addition, nitromethane can be reduced to form methylamine.
3. Stability[21] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[22] Strong reducing agents, acids, alkalis, halogenated alkanes, metal hydrides, metal alkoxides, ammonia, amines, etc.
5. Avoid contact Conditions[23] Vibration, heat
6. Polymerization hazard[24] No polymerization p>
7. Decomposition products[25] Nitrogen oxides
Storage method
Storage Precautions[26] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. The storage temperature should not exceed 37?. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, alkalis, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Methane gas phase nitrification method sprays dilute nitric acid into a mist to vaporize it, and mixes it with preheated methane (natural gas) to maintain a certain ratio of nitric acid, methane, and water vapor. The mixed gas enters the pipeline reactor with molten salt as the heating medium, and is directly nitrified under normal pressure and 450-550°C. The reaction product is condensed and absorbed by water, and the obtained nitromethane aqueous solution is distilled to obtain crude nitromethane, which is then washed and distilled to obtain the finished product. Each ton of product consumes 5,500kg of industrial grade nitric acid and 20,000m3 of natural gas (CH4>95%) (under standard conditions). 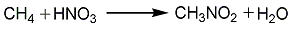
2. Dimethyl sulfate and sodium nitrite reaction method Sodium nitrate and dimethyl sulfate are added to the reactor for reaction, and the reaction product is condensed, distilled, and cooled to stratify to obtain the finished product. In addition, it can also be prepared by reacting sodium nitrite with sodium chloroacetate and then heating. Produced by the reaction of nitrite and alkyl halides. Direct chlorine-phase nitration of other low-carbon alkanes (ethane, propane) can also be used in industry, but the reaction product is a mixture of nitromethane, nitroethane, and nitropropane. 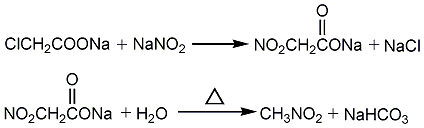
Refining method: Depending on the synthesis method, except for water and nitro In addition to ethane, nitropropane and 2-nitropropane, it may also contain impurities such as aldehydes and alcohols. During refining, it is dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, magnesium sulfate or calcium chloride, and then fractionated. Other refining methods are: add 150mL concentrated sulfuric acid to 1000mL nitromethane, leave it for 1 to 2 days, wash with water, sodium carbonate aqueous solution and water respectively, then dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate for several days, filter and add anhydrous calcium sulfate. Set aside and fractionate before use. You can also reflux nitromethane and activated carbon for 24 hours, while continuously passing nitrogen into the liquid, filtering out the suspended solids, drying and distilling with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and passing the distillate through a column filled with activated alumina. The pure product is obtained by distillation.
3. Distill industrial nitromethane at 13.3kPa to obtain pure nitromethane with a purity of 99.98%.
4. Mix sodium nitrite and dimethyl sulfate and react: 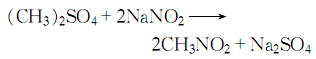
The reaction product is condensed, steam distilled, and left to separate into layers to obtain the finished product. This method has simple process, lower reaction temperature, less corrosive equipment, higher product purity, and the content of superior products can reach more than 99%.
5. Add the sodium carbonate solution to the cold solution of chloroacetic acid at about 15?.?Make the solution pH=8~9, control the temperature below 20?, then add 42% sodium nitrite solution, mix evenly, slowly heat in a reactor with a reflux device until carbon dioxide gas is generated, stop heating, and let The reaction proceeds automatically:
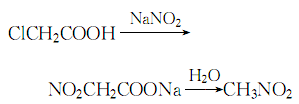
The entire reaction process , control the reaction temperature between 80 and 110°C. Due to the exothermic reaction, when the temperature exceeds 85°C, the heating should be stopped. At 90°C, nitromethane and water are evaporated at the same time. Collect the distillate, let it stand for layering, discard the water layer, dry the oil layer with anhydrous calcium chloride, distill under normal pressure, and collect the 100-101°C fraction. , which is the finished product.
Purpose
1. Nitromethane has great polarity and is miscible with many organic compounds. It is a good solvent and can be used as nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, vinyl resin, polyacrylate paint and beeswax. etc. solvents.
2. It can be used to prepare explosives, rockets, fuels, medicines, dyes, pesticides, fungicides, stabilizers, surfactants and gasoline additives, etc. It is mainly used as a polar solvent in adhesives. It is miscible with many organic compounds and can dissolve cellulose derivatives, resins, dyes, greases, etc., especially for nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, polyacrylonitrile, polyacrylonitrile, etc. Ester, wax products, etc. have good solubility.
3. Used as aerosol propellant, rocket fuel and the manufacture of explosives, dyes, etc.
4. Used as solvent, rocket fuel, gasoline additive and in organic synthesis. [27]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/33-9.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/43968extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/lupragen-n103-catalyst-dimethylbenzylamine-basf/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/65.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44635extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/ethanedioicacid/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-cat-t120-catalyst-nitro/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1738extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/933extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/31-6.jpg