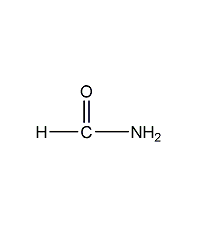
Structural formula
| Business number | 01J1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH3NO |
| Molecular weight | 45.04 |
| label |
Aminoformaldehyde, Methanamide, Carbamaldehyde, Reagents for genetic engineering research, paper treatment agent, Softeners for the fiber industry, Softener for animal glue, Reaction solvents for organic synthesis |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-12-7
MDL number:MFCD00007941
EINECS number:200-842-0
RTECS number:LQ0525000
BRN number:505995
PubChem number:24894985
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent viscous liquid with a slight ammonia smell and hygroscopicity.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa, partially decomposed): 220, 70.5ºC (133.3pa)
3. Melting point (ºC): 2.55~3
4. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4ºC): 1.13339
5. Relative density (g/mL, 25/4ºC): 1.134
6. Relative steam Density (g/mL, air=1): 1.55
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.447
8. Refractive index (25ºC): 1.44682
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 3.764
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 3.302
11. Flash point (ºC, closed): 175
12. Flash point (ºC, open): 150
13. Fire point (ºC): >500
14. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 65.021
15. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 6.699
16. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): -254.1
17. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): 568.6
18. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 2.39
19. Conductivity (S/m): <2×10-1
20. Solubility: Can be dissolved with water, alcohol, ethylene glycol, acetone, acetic acid, dihydrogen Miscible with alkane, glycerin, phenol, etc. But it is almost insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, ethers, chlorinated hydrocarbons, chlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, etc.
Toxicological data
Formamide has an irritating effect on the skin and mucous membranes, can occasionally cause allergies, and can be absorbed by the skin. The oral lethal dose LD for rats is 7500 mg/kg. Rat oral LD50>4000mg/kg. Dermal toxicity in guinea pigs is LD50<5mL/kg and LD50 is 2539mg/kg.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 10.40
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 46.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 109.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 4.12 p>
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): -0.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 43.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 3
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 12.3
10. Isotopic atoms Quantity: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond structure Number of stereocenters: 0
14, Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15, Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: The alkalinity of formamide is very weak, so the salt formed with strong acid is very unstable. Formamide is easily hydrolyzed to ammonium formate in aqueous solution. Ammonium formate is heated and dehydrated to form formamide again:
The hydrolysis rate of formamide is very slow at room temperature, but it is actually relatively stable. However, the hydrolysis rate is relatively fast at high temperatures, especially in the presence of acids and alkalis. There are two ways to pyrolyze formamide: it decomposes into ammonia and carbon monoxide when boiled under normal pressure:
When gaseous formamide is pyrolyzed at 400~600°C in the presence of a dehydrating agent, hydrogen cyanide is obtained , yield 90%:
The adduct formed by formamide and strong acid is very reactive and can undergo the following reactions:
Formamide reacts with alcohol in the presence of hydrogen chloride to form formate. . It reacts with hypochlorous acid in a cold water bath to form N,N-dichloroformamide HCONCl2. This compound is explosive when pure. It reacts with metal potassium and sodium to form a metal compound such as diformamide (HCO)2NH. Photochemical reactions with alkenes produce fatty acid amides. Reacts with alkyl halides at 150°C to form formamide compounds and formic esters:
Formamide reacts with metal salts to form substitutions or adducts:
Formamide reacts with pentoxide Dehydration under the action of diphosphorus produces hydrogen cyanide.
2.This product has low toxicity. Temporarily irritating to skin and mucous membranes. The oral LC50 of mice is greater than 1000mg/kg. Wear protective equipment for long-term exposure.
3. Exist in smoke.
?
Storage method
1. This product should be kept sealed, cool and dry. Keep sealed, avoid contact with water, and store in a cool and ventilated place.
2. Formamide products can be stored and transported in stainless steel or aluminum tanks (tank trucks) or tank-type containers as well as 60kg and 220kg drums. The container material can be polyethylene or polyethylene-lined steel. Keep sealed, avoid contact with water, and store in a cool and ventilated place.
Synthesis method
1. Two-step method: The first step is to generate methyl formate from carbon monoxide and methanol under the action of sodium methoxide. In the second step, methyl formate is ammonolyzed to form formamide, and the reaction conditions are 80-100°C and 0.2-0.6MPa. This method has fewer problems.
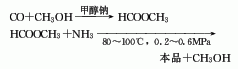
2. Formic acid method Formic acid and methanol First, esterification reaction is performed to generate methyl formate, and then ammonolysis is performed to generate formamide, and then distillation is performed to separate methanol and impurities to obtain the finished product. This method has become obsolete due to its high cost.
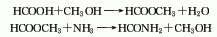
3. One-step method consists of carbon monoxide and Ammonia is catalyzed by sodium methoxide to directly synthesize formamide through high pressure (10-30MPa) and temperature of 80-100?
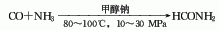
4. Formic acid and urea method.
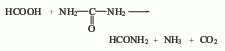
5. The new method consists of sodium formate and Ammonium salt reacts under certain temperature and pressure to form formamide. This method is a domestic patent invention.
Refining method: Formamide is produced on a large scale from carbon monoxide and ammonia at 15~20MPa and 200?. It can also be obtained by heating ammonium formate or the reaction between formate and ammonia. Therefore, it often contains water, ammonia, methanol, formate and ammonium formate. The purity of formamide can be improved by using fractional distillation under reduced pressure or fractional crystallization. Formamide used for determination of physical constants can be refined by adding a few drops of bromothymol blue to formamide. Neutralize with sodium hydroxide, heat the neutralized solution at 80 to 90°C under reduced pressure, and then neutralize. Repeat the operation several times until the solution remains neutral during heating. Then add sodium formate and distill under reduced pressure at 80~90°C. The distillate is neutralized and then distilled, and the next 4/5 fractions are collected to obtain formamide with a melting point of 2.2°C.
6.Ammonium formate is heated and decomposed to obtain formamide, which is then refined through distillation:
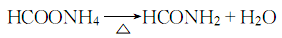
Purpose
1. Formamide has active reactivity and special solubility. It can be used as a raw material for organic synthesis, paper treatment agent, softener in the fiber industry, softener for animal glue, and also used to determine the amino acid content in rice. Analytical reagents. In organic synthesis, it is mostly used in medicine, and it also has many uses in pesticides, dyes, pigments, spices, and auxiliaries. It is also an excellent organic solvent and is mainly used in the spinning of acrylonitrile copolymers and ion exchange resins, as well as in the anti-static coating or conductive coating of plastic products. In addition, it is also used to separate chlorosilanes, purify oils, etc. Formamide can undergo a variety of reactions. In addition to the participation of three hydrogens in the reaction, it can also undergo dehydration, removal of CO, introduction of amino groups, introduction of acyl groups and cyclization reactions. Take Ringhe as an example. Diethyl malonate is cyclized with formamide to obtain the intermediate 4,6-dihydroxypyrimidine of vitamin B4. Anthranilic acid is cyclized with an amide to obtain the antiarrhythmic croroline intermediate quinazolone-4. 3-Amino-4-ethoxycarbonylpyrazole is cyclized with carboxamide to obtain the xanthine oxidase inhibitor allopurinol . The anticancer drug ethyleneimine is obtained by cyclizing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid with formamide. Methyl ethyl methoxymalonate is cyclized with formamide to obtain disodium 5-methoxy-4,6-dihydroxypyrimidine, an intermediate of sulfonamide drugs.
2. Since formamide can dissolve inorganic salts and proteins with high dielectric constants, it can be used in the electrolysis and electroplating industries, as well as as reaction solvents and refining solvents for organic synthesis. In addition, formamide is also used as a raw material for medicines, dyes, spices, etc., as a treatment agent for paper, as a softener in the fiber industry, and as a softener for animal glue.
3.Used as raw material for organic synthesis. Polar solvent for organic reactions. Liquid chromatography solvents and eluents.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44995extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44393extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/dabco-delay-type-catalyst-delay-type-strong-gel-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/78extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/bismuth-neodecanoate/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40279extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40561extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/4-1.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44540extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-cat-ncm-catalyst/