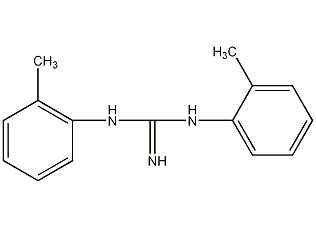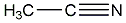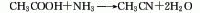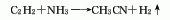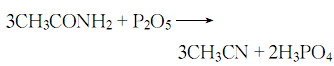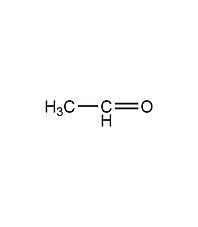
Structural formula
| Business number | 01HX |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H4O |
| Molecular weight | 44.05 |
| label |
anhydrous acetaldehyde, Acetaldehyde, Methanecarbaldehyde, Ethanal, Acetic aldehyde, Aldehyde solvents, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-07-0
MDL number:MFCD00006991
EINECS number:200-836-8
RTECS number:AB1925000
BRN number:505984
PubChem number:24844966
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless liquid with a strong irritating odor. [1]
2. Melting point (?): -123.5[2]
3. Boiling point (?): 20.8[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.788 (16?)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 1.52[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 98.64 (20?)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1166.37[7]
8. Critical temperature (?): 188[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 6.4[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.43[10]
11. Flash point (?): -39 (CC); -40 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (?): 175[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 57[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 4.0[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, miscible in ethanol, ether, Benzene, gasoline, toluene, xylene, etc. [15]
16. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.286
17. Critical volume (cm 3·mol-1): 154
18.Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 11.98
19.Lennard -Jones parameter (K): 141.3
20. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 19.819
21.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 4.490×109
22. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 28.810
23. Liquid phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1165.79
24. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -192.88
25. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 117.3
26. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 89.05
27. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol -1): -1192.48
28. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -166.19
29. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 263.95
30. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol -1): -133.0
31. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1 ): 55.32
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 661mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50 : 13300ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation[17]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg, mild stimulation (open stimulation test)
Rabbit transdermal: 40mg , severe stimulation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [18] Rats and guinea pigs can tolerate 100mg/kg orally for 6 months and reflexes will occur. Movement disorders and increased arterial pressure; oral administration of 10 mg/kg for 2 to 3 months can also cause the same changes.
4. Mutagenicity [19] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 7880?g/dish. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 40 ?mol/L. DNA damage: human lymphocytes 1560 ?mol/L. DNA inhibition: human HeLa cells 10mmol/L. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 1200 ?mol/L.
5. Teratogenicity[20] Rats and mice were given the lowest toxic dose (TDLo) orally or intraperitoneally at different times after pregnancy. Causes developmental malformations in the respiratory system, hepatobiliary system, central nervous system, endocrine system, genitourinary system, musculoskeletal system, and craniofacial system (including nose and tongue).
6. Carcinogenicity [21] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G2B, suspected human carcinogen.
7. Others[22] Minimum intravenous toxic dose in mice (TDLo): 120 mg/kg (administered 7 to 9 days after pregnancy), embryo Mortality rate increases after bubble implantation and is toxic to fetal rats.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[23]
LC50: 37.2mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow); 53mg/L ( 96h) (bluegill sunfish)
EC50: 42mg/L (48h) (water flea); 30.8mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow)
2. Biodegradability [24] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, 80% degradation after 2 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability[25] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 24h (theoretical).
The half-life of photolysis in the atmosphere is 8.4~16h
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 11.50
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 58.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 120.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 17.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 4.55
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 3
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 10.3
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Lively, the carbonyl group in the molecule is easy to undergo addition, cyclization and polymerization reactions. Easily oxidized to acetic acid. Hydrates can be formed in water. It is easy to burn and explode when exposed to open flames or high heat.
2. Acetaldehyde is a flammable and toxic liquid. Irritating to eyes, skin and respiratory organs. Mild poisoning can cause symptoms such as asthma, coughing and headache, while severe poisoning can cause pneumonia and meningitis. Long-term exposure can cause a decrease in red blood cells and an increase in blood pressure. LD50 after oral administration to mice: 1232mg/kg. The maximum allowable concentration in the air at the operating site is 200*10-6. Operators must wear labor protection equipment.
3. Vapor and air form an explosive mixture with an explosion limit of 4.1%~57.0% (volume).
4. Stability[26] Stable
5. Incompatible substances[27] Strong acids, strong oxidants, strong reducing agents, strong bases, halogens, oxygen, flammable substances, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, phosphorus, amines, alcohols, ketones, anhydrides, phenols, etc.
6. Conditions to avoid contact[28] Heating, contact with air
7. Polymerization hazard[29] Aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[30] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 29°C. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, etc. and avoid mixed storage. It should not be stored in large quantities or for long periods of time. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
There are many production methods for acetaldehyde:
1. Ethylene direct oxidation method Ethylene and oxygen are directly oxidized to synthesize crude acetaldehyde in one step through a catalyst containing palladium chloride, copper chloride, hydrochloric acid and water. , and then distilled to obtain the finished product.
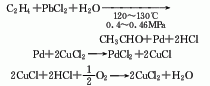
2. Ethanol oxidation method ethanol vapor Acetaldehyde is produced by oxidative dehydrogenation of air using meshes or particles of silver, copper or silver-copper alloy as catalysts at 300-480°C.
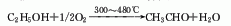
3. Acetylene direct hydration method Acetylene and water are directly hydrated under the action of mercury catalyst or non-mercury catalyst to obtain acetaldehyde. Due to the problem of mercury harm , has been gradually replaced by other methods
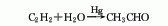
4. Ethanol dehydrogenation method: Under the action of copper catalyst adding cobalt, chromium, zinc or other compounds, ethanol is dehydrogenated to produce acetaldehyde.
5. Saturated hydrocarbon oxidation method.
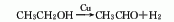
Raw material consumption quota: acetylene hydration law Each ton of product consumes 610kg of 99% acetylene; the ethanol oxidation method consumes 1200kg of 95% ethanol; the ethylene oxidation method (one-step method) consumes 710kg of 99% ethylene and 300 cubic meters of oxygen (99%). Commercially available industrial products acetaldehyde, ethylene method acetaldehyde. The purity of aldehyde is 99.7%, and the purity of ethanol method is 98%.
6. Preparation method:

In the reaction bottle equipped with a fractionation device (the receiving bottle is cooled with an ice bath to reduce the volatilization loss of acetaldehyde), add paraacetaldehyde ( 2) 50g, 0.5 mol of concentrated sulfuric acid, a few grains of zeolite. Heat slowly, being careful not to make the temperature at the top of the fractionation column too high. The reaction should proceed slowly, because acetaldehyde and paraacetaldehyde can form an azeotrope, bp42. ? (molar ratio is acetaldehyde: paraacetaldehyde = 53.4:46.6). Most of the acetaldehyde (1) is evaporated at 21 ~ 25 ?. Stop distillation when there is approximately 10 mL left in the reaction bottle (if it is distilled to dryness) Risk of explosion). The acetaldehyde prepared in this way can meet most uses. If higher purity acetaldehyde is required, fractionation can be carried out again and the 21°C fraction can be collected.
7. Preparation method:
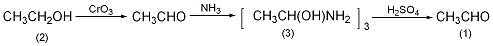
In a reaction bottle equipped with a ventilation tube, a dropping funnel, and a distillation device (the receiving bottle can be filled with two gas washing bottles connected in sequence, filled with ether, and cooled with an ice-salt bath), add 135 mL (about 2 mol) of ethanol (2) ), add 1/3 volume of dilute sulfuric acid composed of 150mL concentrated sulfuric acid and 250mL water. Pour in carbon dioxide gas and heat to boiling. After diluting another 2/3 volume of sulfuric acid with 100 mL of water, add 200 g of sodium dichromate, stir to dissolve, and drop this solution into the reactant. The reaction is exothermic. The generated acetaldehyde is continuously taken out by the carbon dioxide gas flow, and the acetaldehyde is dissolved in ether. Complete the dripping in about 30 minutes, and then continue to pass carbon dioxide for 10 minutes. A solution of acetaldehyde in diethyl ether was obtained. Acetaldehyde cannot be distilled from its ether solution. To obtain pure acetaldehyde, proceed as follows: cool the acetaldehyde ether solution in an ice-water bath, slowly pass in dry nitrogen, and shake continuously. During this period, acetaldehyde amine crystals precipitate until the precipitation is complete ?. Filter with suction, wash with anhydrous ether, and dry to obtain 55g of acetaldehydeamine (3). In a reaction bottle equipped with a ventilation tube, a dropping funnel, and a distillation device (the receiving bottle is cooled with an ice-salt bath), add compound (3), dissolve it in 50 mL of water, add carbon dioxide gas, heat it in the water bath, and dropwise add 60 mL of concentrated solution. The acetaldehyde produced by dilute sulfuric acid mixed with sulfuric acid and 80 mL of water is continuously evaporated, and the dripping is completed in about 30 minutes. The boiling point of acetaldehyde is 21°C. Note: ? Take a small amount of transparent liquid and add nitrogen until it is saturated. If no precipitation precipitates, it means the reaction is over. [33]
Purpose
1. Used to prepare standard solutions, reducing agents, and bactericides when measuring aldehydes using colorimetric methods. Manufacture of paraacetaldehyde, acetic acid, butanol and pentaerythritol. Organic synthesis intermediates and solvents.
2. Industrially used to produce paraformaldehyde, acetic acid, ethyl acetate, pentaerythritol, plastics, synthetic rubber, synthetic resin, etc. It can also be used for spectrophotometric determination of aldehydes.
3. Reducing agent, bactericide, used to prepare standard solution when measuring aldehyde by colorimetric method. Industrially used to make polyacetaldehyde, acetic acid, synthetic rubber, etc.
4. Used to make acetic acid, acetic anhydride and synthetic resin. [31]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44319extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-nem-niax-nem-jeffcat-nem/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/category/morpholine/page/4/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-pc5-catalyst-cas3030-47-5-newtopchem/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/182extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-eg-33-triethylenediamine-in-eg-solution-pc-cat-td-33eg/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39593extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-cat-dmi-catalyst-nitro/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/teda-l33b-polyurethane-amine-catalyst-tosoh/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39736