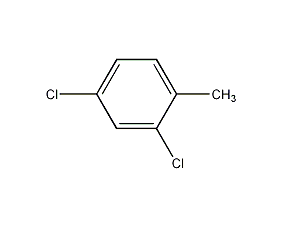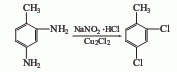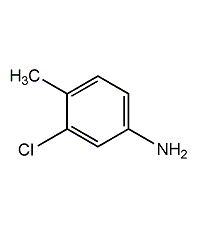
Structural formula
| Business number | 029Q |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H8ClN |
| Molecular weight | 141 |
| label |
None |
Numbering system
CAS number:95-74-9
MDL number:MFCD00007773
EINECS number:202-446-3
RTECS number:XU5111000
BRN number:636511
PubChem number:24854163
Physical property data
1. Properties: yellow or brown liquid
2. Density (g/mL, 20?): 1.17
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air = 1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 26
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 237-238.5
6. Boiling point (ºC, 1.60kPa): 113-114
7. Refractive index: 1.584
8. Flash point (ºC): 100
9. Specific optical rotation Degree (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): >500
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg,ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC) : Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Dissolved in In ethanol or benzene, it is slightly soluble in hot water and insoluble in cold water.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 1500mg/kg; rat intraperitoneal LD50: 325mg/kg; rat intravenous LD50: 48mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 13mg/kg; pigeon viagra Oral LD50: 13 mg/kg; Oral LD50 of quail: 1 mg/kg; Oral LD50 of wild birds: 2400 ?g/kg;
2. Mutagenicity
Oral administration of rats DNA synthesis: 100 mg/kg;
Oral mutation test in mice: 300mg/kg
Oral DNA inhibition in rats: 200 mg/kg;
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment and it is recommended not to let it enter the environment.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.20
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 119.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 306.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 42.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 15.94
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. ComplexImpurity: 94.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determined number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain atomic stereocenter Quantity: 0
13. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Covalent bonds Number of units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid light and contact with strong oxidants, acids, acid anhydrides, and acid chlorides.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from chlorination and reduction of p-nitrotoluene. 1. Chlorination Add nitrotoluene to the reaction pot, heat to 75°C, add anhydrous ferric chloride and iodine, stir for 10-20 minutes, start chlorine flow at 60°C, and keep the chlorination temperature at 55-70°C , when the melting point of chloride is >58.5°C and does not grow within 20 minutes. Catch the air, raise the temperature to 80-90°C, and keep it for 1.5-2 hours to obtain 2-chloro-4-nitrotoluene with a yield of 98%. 2. Reduction: Add the prepared sodium sulfide solution into the reaction pot, add the above-mentioned 2-chloro-4-nitrotoluene at 70-80°C, reflux for 4 hours, the temperature is 110±5°C, the purity of the amine oil is >98.5%, melting point When >19°C, distill to obtain the finished product with a yield of 90%. If iron powder is used for reduction, the reaction temperature is about 100°C, and the reactants are extracted with toluene. The yield is about 95%.
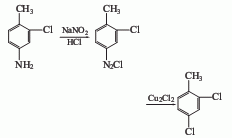
2. The preparation method is to add molten 3-chloro-4-methylnitrobenzene and solvent into the autoclave, and then pump a certain amount of catalyst and distilled water into the autoclave under negative pressure. The hydrogenation reaction is catalyzed under a certain temperature and pressure, and then the materials are pumped into the storage tank, left to stand and stratified, and the materials are rectified in the distillation kettle to obtain the solvent and the finished product respectively.
You can also use sodium sulfide for reduction. Add sodium sulfide to the reaction pot, add 3-chloro-4-methylnitrobenzene at 70~80°C, reflux for 4 hours, and the temperature is (110±5)°C, and the reaction After completion, the mixture is separated into layers and distilled to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
Organic synthesis intermediate, used in the production of organic pigment intermediate 2B acid and pesticide chloromylon.
extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/tris3-dimethylaminopropylamine-cas-33329-35-0/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44594extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/organic-mercury-replacement-catalyst-nt-cat-e-at/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-25-s-catalyst-cas280-57-9-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/917extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/pc-cat-tka-polyurethane-metal-carboxylate-catalyst-polycat-46/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/37-4.jpgextended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/cas-7560-83-0/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/93extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/129-2.jpg