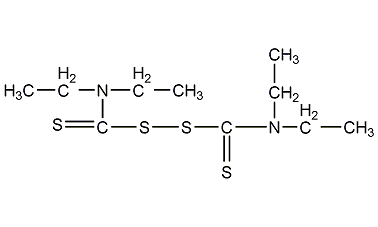
Structural formula
| Business number | 02CP |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H20N2S4 |
| Molecular weight | 296.55 |
| label |
accelerator TETD, Tetraethylthioperoxydicarbonate diamide, Tetraethylthiuram disulfide, Bis(diethylthiocarbamyl) disulfide, Accelerator TETD, 4 ethyl carbonate peroxide amide, Tetraethyl thiuram disulfide disulfide Long, Disulfide bis (diethyl thio carbamoyl), accelerator |
Numbering system
CAS number:97-77-8
MDL number:MFCD00009048
EINECS number:202-607-8
RTECS number:JO1225000
BRN number:1712560
PubChem number:24278722
Physical property data
1. Character: yellow-white crystal
2. Density (g/mL, 20?): 1.17
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1 ): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 65?70
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Not determined
7. Refractive index: Not determined
8. Flash point (ºC): Not determined
9. Specific rotation Degree (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): 890
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in water , slightly soluble in acetone, soluble in benzene, chloroform, and carbon disulfide.
Toxicological data
1. Irritation: Rabbit eye: 100mg, mild irritation.
2. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD5O: 8600mg/kg
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 86.39
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 246.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 675.7
4. Surface expansion?? (dyne/cm): 56.9
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3 ):
7. Polarizability: 34.24
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 7
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 121
7. Number of heavy atoms: 16
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 201
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants.
2. Soluble in acetone, benzene, toluene, carbon disulfide and chloroform, slightly soluble in ethanol and gasoline, insoluble in water, dilute acid and dilute alkali. Irritating to skin and mucous membranes. Storage stable.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. The packaging is sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Preparation of sodium diethyldithiocarbamate: Add diethylamine and carbon disulfide to an alkali solution with a density of 1.075kg/m3 (10°Bé) under stirring, and heat to 40~45°C for condensation reaction 2h, when the pH value is constant, it is the end point of the reaction. The reaction produces sodium diethyldithiocarbamate.
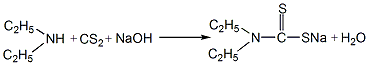
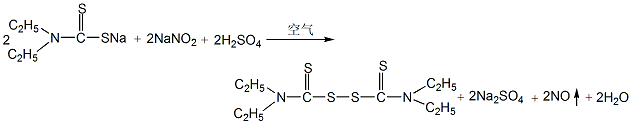
2. Preparation of accelerator TETD. Add 10% sodium nitrite aqueous solution dropwise to the product of the previous reaction at room temperature, stir and mix evenly, and the material will turn into a grass green color. After filtering out the residue, 4% dilute sulfuric acid was added dropwise, and air was blown in to control the reaction temperature below 10°C. The accelerator TETD produced by the reaction is precipitated as solid particles. After the reaction is complete, the material is discharged and filtered, and the filter cake is washed, centrifugally dehydrated, dried, and screened to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
Used as super accelerator and vulcanizing agent for natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, nitrile rubber, butyl rubber, butadiene rubber and latex.
Commonly used in the manufacture of cables, medical supplies, tapes, rubber shoes, inner tubes, colorful products, etc.
In addition, it can also be used as a fungicide and insecticide.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/69extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/lupragen-n301-catalyst-pentamethylenediethylenetriamine-basf/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/low-odor-reactive-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39385extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/54.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-33-S-Addocat-106-TEDA-L33B.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/lupragen-n104-catalyst-ethylmorpholine-basf/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dimethylaminoethoxyethanol-cas-1704-62-7-n-dimethylethylaminoglycol/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/cas-26761-42-2/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/nn-dicyclohexylmethylamine/