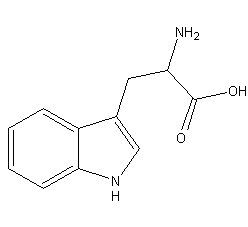
Structural formula
| Business number | 0167 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C11H12N2O2 |
| Molecular weight | 204.23 |
| label |
DL-?-(3-indolyl)-?-aminopropionic acid, Mixed Tryptophan, DL-2-amino-3-indolyl-1-propionic acid, DL-Aminoindolepropionic acid, DL-trypsin amino acid, (±)-2-Amino-3-(3-indoyl) propionic acid, DL-3?-Indolylalanine, amino acid additives, amino acid drugs, intermediates, Biochemical reagents |
Numbering system
CAS number:54-12-6
MDL number:MFCD00064339
EINECS number:200-194-9
RTECS number:YN6129200
BRN number:86199
PubChem number:24900128
Physical property data
1. Properties: White to yellow-white crystals or crystalline powder, odorless or slightly smelly, slightly sweet taste. The bitterness of the L-type and the sweetness of the D-type are similar to sucrose. Poor acid resistance and light resistance.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4?): 1.362
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 289~290
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined Determined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturation Vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (% , V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in water (solubility 0.4 at 25°C %), dilute acids and bases, slightly soluble in ethanol
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: mouse abdominal LC50: >1 mg/kg
2. Carcinogenicity: rat oral TDLo: 844mg/kg/92W-C
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 57.76
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 149.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 435.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 71.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 22.90 p>
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -1.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 79.1
p>
7. Number of heavy atoms: 15
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 245
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Found in tobacco leaves.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored away from light.
Synthesis method
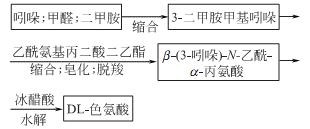
1. Indole is condensed to form pyridamine (3-dimethylaminomethylindole), which is further condensed to form ?-carboxylic acid ethyl ester-?(3-indole)-N-acetyl-?- Alanine ethyl ester undergoes hydrolysis, decarboxylation, and rehydrolysis to generate DL-tryptophan.
2.Using indole as raw material, tryptophan is produced under enzyme catalysis in a high-concentration pyruvate and ammonia atmosphere. Or from indole and acetamidomalonate ethylene glycol.
3.
Purpose
1. Nutritional and biochemical research. Prepare tissue culture medium. Nutritional supplements and antioxidants can be added to foods with low tryptophan content such as gelatin and corn. Combined with lysine, methionine and threonine in beef, rice, corn, etc., the best results can be obtained. L-tryptophan is obtained by optical refraction of DL-tryptophan, which is an important component of amino acid infusions and comprehensive amino acid preparations, and can treat niacin deficiency. As a feed additive, it participates in the renewal of plasma proteins in animals, promotes the function of riboflavin, contributes to the synthesis of nicotinic acid and heme, can significantly increase antibodies in the fetuses of pregnant animals, and has a stimulating effect on dairy cows and sows during lactation. The role of milk. When livestock and poultry lack tryptophan, their growth stagnates, their weight decreases, their fat accumulation decreases, and their testicles atrophy. 2.Used as a feed nutritional fortifier, it can significantly increase the body antibodies of animal fetuses and promote the milk production of dairy cows and sows during the lactation period. When animals lack tryptophan, their growth stagnates, their weight decreases, and their fat accumulation decreases. It is mainly used in artificial milk for piglets, and a small amount is used in sows and laying hens. The general dosage is 0.02% to 0.05%.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/839extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fentacat-b12-catalyst-cas111-42-2-solvay/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/45168extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/catalyst-8154-polyurethane-delayed-catalyst-8154/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44821extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/potassium-neodecanoate-2/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-t96-catalyst-cas103-83-3-newtopchem/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/16extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/reactive-catalyst-dabco-reactive-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44583