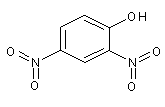
Structural formula
| Business number | 014M |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H4N2O5 |
| Molecular weight | 184.11 |
| label |
?-dinitrophenol, 2-nitrophenol, 2-Dinitrophenol, a-Dinitrophenol, Acid-base indicator |
Numbering system
CAS number:51-28-5
MDL number:MFCD00007115
EINECS number:200-087-7
RTECS number:SL2800000
BRN number:1246142
PubChem number:24861147
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow crystal or powder [1]
2. Melting point (?): 114~115[ 2]
3. Boiling point (?): sublimation[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.68[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 6.35[5]
6. Heat of combustion ( kJ/mol): -2708.6[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.54~1.67[7]
8. Solubility: Insoluble in cold water, soluble in hot water, ethanol, ether, acetone, benzene, and chloroform. [8]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[9]
LD50: 30mg/kg (rat oral); 72mg/kg (oral in mice); 700mg/kg (transdermal in guinea pigs)
2. Irritation[10] Rabbit transdermal: 300mg (4 weeks, intermittent), mild stimulation.
3. Mutagenicity[11]
Microbial mutagenicity: Escherichia coli 200ppm (3h). DNA inhibition: hamster lung 7mmol/L. DNA damage: rat liver 100 ?mol/L.
4. Others[12] The lowest toxic dose in the abdominal cavity of mice (TDLo): 40800?g/kg (pregnant 10 ~12d), embryotoxic.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[13]
LC50: 0.62mg/L (96h) (Bluegill Sunfish); 0.7mg/L (96h) (Atlantic salmon); 6.58~13.3mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow, dynamic); 4.85mg/L (96h) (sugar shrimp); 4.09~4.71mg/ L (96h) (Daphnia); 98mg/L (96h) (Skeletonema costatum)
2. Biodegradability[14]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 1622~6312
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 68~170
3. Non-biodegradability[15]
Photolysis maximum light absorption (nm): 365
The half-life of photooxidation in water (h): 77~3840
The half-life of photooxidation in air (h): 111~1114
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 41.22
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 111.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 333.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 79.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 16.34
planCompute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 4
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 112
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 220
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[16] Stable
2. Incompatible substances [17] Strong oxidants, strong bases, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, heavy metal powders
3. Conditions to avoid contact [18] Friction, impact, heat
4. Polymerization hazards[19] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[20] Nitrogen oxides p>
Storage method
Storage Precautions[21] Store in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement the “two people to send and receive, and two people to keep” system. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 35?. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the hydrolysis of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene in alkaline solution. Add 1400L water to the hydrolysis pot, stir and heat to 60°C, and add 750kg of melted 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene into the pot. Continue to raise the temperature to 90°C, and gradually add 780L of 30% sodium hydroxide solution within 1.5 hours. When the temperature rises during feeding, control the temperature not to exceed 102-104°C and keep it warm for 30 minutes. Cool and filter the precipitated sodium salt. Dissolve in water, acidify to pH 1, and yellow crystals of 2,4-dinitrophenol will precipitate. Another preparation method is obtained by low-temperature nitration of phenol. Mix 67% sulfuric acid, 53% nitric acid and phenol evenly below 30°C, and then heat to 90°C with stirring. The mixture begins to react violently and releases nitrogen oxide to control the reaction speed and reduce the loss of reactants. After the reaction eases, heat for 30 minutes, cool, filter, and wash with water to obtain the product. Refining can be done by acid-base method or recrystallization with ethanol.
2.After heating the water to 60?, add melted 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (chlorobenzene: water?1 ? 2), stir and raise the temperature to 90°C, then add 35% sodium hydroxide solution in batches until no oil beads exist after the reaction is completed. During the reaction process, the reaction temperature should be controlled not to exceed 102~104?:
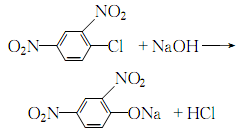
After adding the sodium hydroxide solution, keep it warm for 30 minutes, and stir continuously until the oil layer disappears and the hydrolysis reaction is complete. Leave to stand, cool and crystallize until complete. Dissolve the filtered 2,4-dinitrophenol sodium salt with an appropriate amount of warm water, then add hydrochloric acid until the ph value is 1. Precipitate 2,4 dinitrophenol:
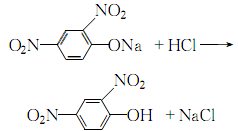
The obtained crystals are washed with a small amount of cold water until they are neutral. Then recrystallize with hot water
Purpose
1. Mainly used in the production of sulfur dyes, such as sulfur black BN; BRN; 2BRN, etc. Also used in the production of picric acid and developer. It is used as an acid-base indicator in analytical chemistry, and the color change range is pH=2.8 (colorless)-4.4 (yellow); it can also be used to detect potassium, ammonium, magnesium, etc.
2. Used in organic synthesis, dyes, explosives, etc. [22]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/567extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/997extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-ne300-catalyst-cas10861-07-1-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/3extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/author/newtopchemextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fomrez-ul-24-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-BLX-11-polyurethane-foaming-catalyst-foaming-catalyst.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Dimethyl-tin-oxide-2273-45-2-CAS2273-45-2-Dimethyltin-oxide.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Di-n-octyltin-dilaurate-CAS3648-18-8-DOTDL.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39817